Do you know how to treat water?
Today Susan will introduce to you a piece of professional water treatment knowledge - the causes and solutions of reverse osmosis membrane fouling.
 ONE. Technical analysis of reverse osmosis membrane fouling
ONE. Technical analysis of reverse osmosis membrane fouling
Reverse osmosis membrane fouling is a complex phenomenon, which involves several interrelated but different factors. For reverse osmosis systems with pretreatment systems, regular cleaning can greatly restore the water output of the membrane. If the pretreatment system is unreasonable, cleaning will not have a significant effect on restoring the performance of the reverse osmosis components, and the number of cleanings will increase, but frequent cleaning cannot replace reasonable reverse osmosis system pretreatment.

The fouling of the reverse osmosis membrane can be seen from the changes in the main parameters of the reverse osmosis components, such as the salt permeation, two-stage pressure drop, and water production, and the comprehensive changes of these parameters. Under the stable operation of the reverse osmosis system, the salt permeation and membrane pressure drop basically do not change with time, and the cause of the fouling of the reverse osmosis membrane can often be identified.
The long-term successful operation of the reverse osmosis system depends on three factors: pretreatment, system design, operation and maintenance.

All three factors are important. The reasonable selection of the pretreatment system is the basis for the reasonable design and safe operation of the reverse osmosis equipment; without pretreatment, any type of water entering the reverse osmosis will have an adverse effect on the reverse osmosis equipment. The purpose of pretreatment is to remove or reduce the fouling particles in the reverse osmosis water.
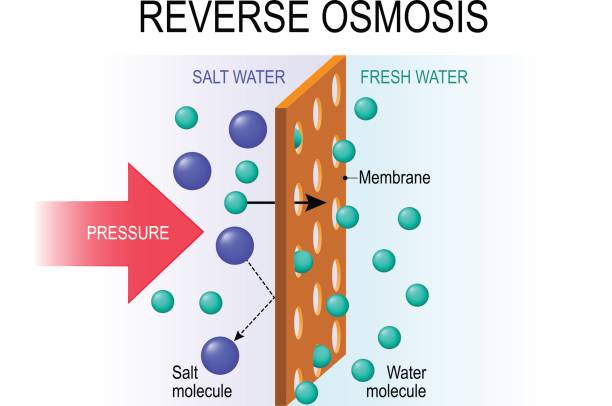
Some of these fouling substances affect the inside of the reverse osmosis component, and some are chemical deposits formed on the membrane surface. The fouling substances have different effects on reverse osmosis, and the treatment methods are also different. The relevant issues about the pretreatment of the reverse osmosis system are applicable to at least 95% of the pollution problems of the reverse osmosis membrane. There are also some other types of pollution, such as deposition formed by H2S oxidation and precipitation caused by organic compounds.
TWO . Eight reasons for the fouling of reverse osmosis membranes
1. Concentration polarization
In the reverse osmosis desalination system, the selective permeability of the membrane causes water molecules to continuously pass through the membrane from the high-pressure side, while the solute molecules still remain in the original solution, resulting in a concentration difference between the feed liquid on the membrane surface and the inlet feed liquid. In severe cases, a very high concentration gradient will be generated. This phenomenon is called concentration grading. Concentration grading increases the osmotic pressure of the feed liquid and reduces the effective driving force, resulting in a decrease in water permeability and desalination rate.
2. Inorganic salt scaling
Salts with smaller solubility products such as CaCO3, CaSO4, BaSO4, SrSO4, CaF2 and SiO2 may precipitate due to concentration exceeding their solubility products during the reverse osmosis process, resulting in sediments remaining on the membrane surface or forming scale in the water inlet channel.
3. Adsorption pollution
Some well water sources belonging to the bitter and salty water range generally contain low-valent iron ions and manganese ions, which have certain reducing properties. The main reason for membrane fouling caused by such water sources is that iron, aluminum, manganese, etc. produce colloidal particles on the membrane surface. When O2 enters the inlet water containing Fe2+, the high alkalinity water source forms iron carbonate and iron silicate, and reducing bacteria are mixed in. Iron scale forms faster and faster, and colloidal iron caused by the conversion of iron flocculants. The characteristic performance after metal pollution is a decrease in water production and an increase in pressure difference.
 4. Formation of biological sludge
4. Formation of biological sludge
Water sources derived from surface water and sewage are mostly biological sludge. When the membrane surface is covered with vigorous microbial sludge, the salts removed by the membrane will be trapped in the sticky layer and not easily washed away by water, providing rich nutrients for microbial reproduction. At the same time, the scale inhibitors and water softeners added during the pretreatment of reverse osmosis water can promote the growth of microorganisms.
5. Colloidal pollution
Both groundwater and surface water contain iron, aluminum, silicon, organic matter and other substances. They form colloids with coagulants, coagulants, scale inhibitors and other substances added during pretreatment and deposit on the membrane surface to cause colloidal pollution. Colloidal pollution is difficult to handle because it carries the same charge, is relatively stable, and is not easy to settle. However, when the RO membrane filters water, it is retained on the membrane surface to form hydrates, which easily pollute the membrane and cause a decrease in water flux. This trend is generally evaluated by the pollution index (SDI). Usually when SDI is less than 3, this type of pollution does not occur on the membrane surface; when SDI is greater than 3, fouling will occur.
6. Water hammer phenomenon
For the reverse osmosis system, due to unreasonable design, there is a large amount of air in the membrane shell of the membrane at the beginning of the debugging stage. When the liquid to be treated enters the membrane shell instantly, the air is compressible and it is impossible to completely exhaust it instantly; when the air reaches a certain pressure in the membrane shell, it will suddenly burst and release, causing the reverse osmosis membrane to collide, squeeze and move with each other in the membrane shell, resulting in the "water hammer" phenomenon. In the reverse osmosis system, the harm of water hammer is to cause irreversible damage to the reverse osmosis membrane element. Of course, this phenomenon can also be avoided through perfect design.
7. Suspended particles
The security filter may cause leakage of filter media, corrosion debris and foreign matter (such as small core wool line) due to "short circuit" or defects, or incomplete flushing of reverse osmosis for the first time, which may cause the membrane element to be contaminated, the water inlet channel to be blocked, and amorphous precipitation to form on the membrane surface. But this situation is rarely encountered.
8. Pollution caused by other factors
Hydrocarbons and silicone-based oils and lipids cover the membrane surface, causing the membrane to be polluted; membrane hydrolysis, organic solvents and oxidizing substances can also cause essential changes in the membrane material.
THREE. Anti-scaling treatment of reverse osmosis membrane
The scaling of reverse osmosis membrane is caused by the deposition of insoluble salts as the influent water is concentrated into concentrated water. In the reverse osmosis process, the concentration of salts in the influent may exceed the upper limit of solubility and produce precipitation. In brackish water, CaCO3 needs to be treated. In seawater and brackish water, the salts that will not exceed the upper limit of solubility after reverse osmosis concentration are calculated to be BaSO4, SrSO4, CaF2, and SiO2.
If the insoluble salt exceeds the upper limit of solubility, one or more of the following methods need to be adopted for treatment:
Reduce the desalination rate;
Use ion exchange softening to remove Ca2+;
Use acid addition to remove carbonate and bicarbonate;
Add reverse osmosis scale inhibitor.
FOUR. Solutions to reverse osmosis membrane fouling
1. Improve pretreatment
For each membrane device, users hope that it can work effectively, hope to have a high desalination rate, a large water permeability and as long a life as possible. To achieve the above three points, the quality of the water supply is crucial, so the raw water entering the membrane device must be well pretreated. Reasonable pretreatment is very important for the long-term safe operation of the reverse osmosis device. With pretreatment that meets the reverse osmosis inlet water quality requirements, it can ensure that the water flow rate remains stable, the desalination rate remains at a certain value for a long time, the product water recovery rate can remain unchanged, the operating costs are reduced, and the membrane service life is longer.
Specifically, the purpose of reverse osmosis pretreatment is as follows:
(1) Prevent contamination on the membrane surface, that is, prevent suspended impurities, microorganisms, colloids, etc. from adhering to the membrane surface or fouling the water flow channel of the membrane element.
(2) Prevent scaling on the membrane surface. During the operation of the reverse osmosis device, due to the concentration of water, some insoluble salts are deposited on the membrane surface, so the formation of these insoluble salts must be prevented.
(3) Ensure that the membrane is protected from mechanical and chemical damage so that the membrane has good performance and a sufficiently long service life.
2. Clean the membrane
Although the feed liquid has undergone various pretreatment measures, the membrane surface may still produce deposition and scaling after long-term use, causing the membrane pores to be blocked and the water output to decrease. Therefore, it is necessary to clean the polluted membrane regularly. However, the reverse osmosis membrane system cannot wait until the pollution is very serious before cleaning, which will increase the difficulty of cleaning, increase the number of cleaning steps and prolong the cleaning time. It is necessary to correctly grasp the cleaning time and remove the dirt in time.
 ① Cleaning principle
① Cleaning principle
Understand the local water quality characteristics, conduct chemical analysis of pollutants, and select scientific cleaning agents and cleaning methods through result analysis to provide a basis for finding the ideal method under specific water supply conditions.
② Cleaning conditions
A. The product water volume is 5%-10% lower than normal.
B. In order to maintain the product water volume, the water supply pressure after temperature correction is increased by 10%-15%.
C. The conductivity of the permeate water (increased salt content) increases by 5%-10%.
D. For multi-stage RO systems, the pressure drop through different stages increases significantly.
③Cleaning method

First, backflush the system;
Then, perform negative pressure cleaning;
Perform mechanical cleaning if necessary;
Then perform chemical cleaning;
If conditions permit, ultrasonic cleaning can be performed;
Online electric field cleaning is a good method, but it is expensive;
Because chemical cleaning is more effective, some other methods are not easy to implement, and although the names and usage methods of the agents provided by various suppliers are different, their principles are roughly the same.
④Cleaning steps:
A. Prepare cleaning solution;
B. Low-flow input cleaning solution;
C. Circulation;
D. Soaking;
E. High-flow water pump circulation;
F. Rinse;
G. Restart the system.
Cleaning for special pollutants:
Cleaning sulfate scale, cleaning carbonate scale, cleaning iron and manganese pollution, cleaning organic pollution, etc.
3. Suitable maintenance of the membrane
New reverse osmosis membrane elements are usually soaked in 1% NaHSO3 and 18% glycerol aqueous solution and stored in sealed plastic bags. If the plastic bag is not broken, it can be stored for about 1 year without affecting its life and performance. Once the plastic bag is opened, it should be used as soon as possible to avoid oxidation of NaHSO3 in the air and adverse effects on the components. Therefore, the membrane should be opened before use as much as possible.
During the non-production period, the maintenance of the reverse osmosis system is a relatively important issue, which can be carried out in the following way.
(1) The system is shut down for 1-3 days in a short period of time.
Before shutting down, flush the system at low pressure (0.2-0.4MPa) and high flow rate (approximately equal to the system's water output) for 14-16 minutes. Maintain normal natural water flow and let water flow into the concentrated water channel.
(2) The system is shut down for more than one week.
Before shutting down, flush the system at low pressure (0.2-0.4MPa) and high flow rate (approximately equal to the system's water output) for 14-16 minutes. Perform chemical cleaning according to the system chemical cleaning method in the reverse osmosis system operating manual. After the chemical cleaning is completed, rinse the reverse osmosis membrane. Prepare 0.5% formalin solution, input it into the system at low pressure, and circulate it for 10 minutes. Close all system valves and seal them. If the system is shut down for more than 10 days, the formalin solution must be replaced every 10 days.
(3) The ambient temperature is lower than 5°C
Before shutting down, flush the system with low pressure (0.2-0.4MPa) and large flow (approximately equal to the system's water output) for 14-16 minutes. If conditions permit, the ambient temperature can be raised to above 5°C, and then the system maintenance can be performed according to method 1. If there is no condition to raise the ambient temperature, use low pressure (0.1MPa) and a flow rate of 1/3 of the system's water output for a long time to prevent the reverse osmosis membrane from being frozen, and ensure that the system is operated for 2 hours every day. After cleaning the reverse osmosis membrane, remove the reverse osmosis membrane and move it to a place where the ambient temperature is greater than 5°C. Soak it in the prepared 0.5% formalin solution and turn it over every two days. The water in the system pipeline should be drained clean to prevent damage to the system due to freezing.
4, Avoid running the membrane under high pressure
When the system is started and stopped, there is residual gas remaining, so that the system is operated under high pressure.
The pressure gauges before and after the filter in the system are used to monitor the pressure drop of the filter element, and the primary and final pressure gauges are used to monitor the pressure drop of the RO membrane assembly. Adjust the water inlet valve and the concentrate valve to ensure the operating pressure and recovery rate. If the water flow rate or total flow rate decreases during operation, or the pressure difference between the primary and secondary stages increases significantly compared to the pressure difference at the beginning of operation (based on the data of the initial operation of the new reverse osmosis membrane assembly), the system needs to be flushed or cleaned to ensure the good performance of the membrane assembly.
 (1) After the equipment is emptied and restarted, the remaining air should be exhausted under the system pressure before gradually increasing the pressure.
(1) After the equipment is emptied and restarted, the remaining air should be exhausted under the system pressure before gradually increasing the pressure.
(2) When the joint between the pretreatment equipment and the high-pressure pump is not well sealed or leaking, some air will be sucked into the poorly sealed area due to vacuum. The micron filter should be cleaned or replaced to ensure that the pipeline is leak-free.
(3) Check whether the operation of each operating pump is normal and whether the flow rate is the same as the specified value, and compare it with the pump operation curve to determine the operating pressure.
5. Pay attention to the operation when shutting down
(1) Rapid pressure reduction without flushing when shutting down. Since the concentration of inorganic salts on the concentrate side of the membrane is higher than that of the raw water, it is easy to scale and contaminate the membrane. When preparing to shut down, gradually reduce the pressure to about 3 bar and rinse with pre-treated water for 14 to 16 minutes.
(2) When preparing to shut down, adding chemical reagents will cause the reagents to remain in the membrane and membrane shell, causing membrane contamination and affecting the service life of the membrane. Dosing should be stopped.
I hope it can be helpful to you. If you want to know more about the common sense of water treatment, please leave a message in the comment area, I will try my best to reply. If you want to know more about water treatment knowledge or want to buy related water purification equipment and air purification equipment, please contact me through the following business card. Thank you for reading and wish you a happy life!










 How to choose a filtered water purifier: help you buy the best water purifier! Keep your water as pure as it can be!
How to choose a filtered water purifier: help you buy the best water purifier! Keep your water as pure as it can be!
 Analysis and solutions to the causes of reverse osmosis membrane fouling
Analysis and solutions to the causes of reverse osmosis membrane fouling
 Do you know how to extend the life of your reverse osmosis membrane?
Do you know how to extend the life of your reverse osmosis membrane?
 How much do you know about ultrafiltration technology and ultrafiltration membranes?? Ultrafiltration Knowledge Points Collection, you deserve it!
How much do you know about ultrafiltration technology and ultrafiltration membranes?? Ultrafiltration Knowledge Points Collection, you deserve it!